In the modern world of technology, flexible displays are revolutionizing how we interact with our devices. These displays, often seen in smartphones, wearables, and televisions, have changed the way we think about screen technology.
Among the most intriguing features of flexible bendable monitors displays are their curvature and viewing angles, which allow for a more immersive and adaptable user experience. But what exactly is the science behind these flexible display curvatures and the effects they have on viewing angles?
Understanding Flexible Displays
Before diving into curvature and viewing angles, it’s important to understand what flexible displays are and how they work. Flexible displays are a type of screen technology that can bend or flex without losing their display quality. These displays use materials like organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) or electronic paper that are thin, lightweight, and capable of being molded or bent without damaging the structure.
Unlike traditional rigid screens made from glass or plastic, flexible displays use materials that can bend and stretch. This flexibility allows the display to be used in various applications, including curved screens, foldable devices, and even wearable technology.
Key Features of Flexible Displays:
- Bendability: They can be bent or twisted without breaking.
- Durability: Flexible displays are often more resistant to damage from impact or pressure.
- Lightweight: These displays are thinner and lighter than traditional screens.
- High-Quality Resolution: Despite their flexibility, flexible displays offer high-definition resolution with vibrant colors.
Now, let’s explore the key aspects of flexible displays, curvature and viewing angles.
The Science of Flexible Display Curvature
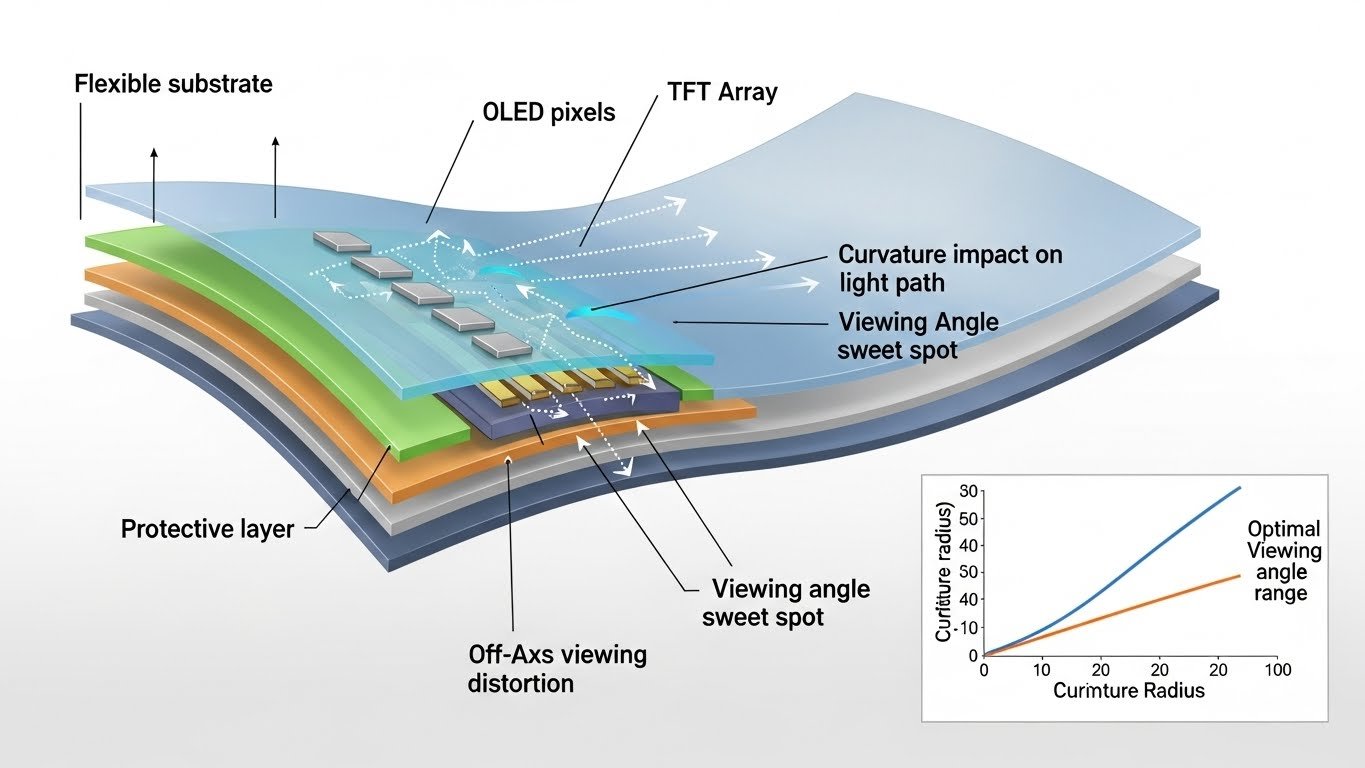
Curvature in flexible displays refers to the ability to bend or shape the display to fit a specific design. This is one of the most prominent features in devices like curved televisions, folding monitor smartphones, and even wearable devices like smartwatches. The science behind this curvature involves the materials used in flexible screens and the technology that allows these screens to bend without compromising functionality.
Flexible displays typically rely on OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) or AMOLED (Active Matrix OLED) technology. OLED screens consist of organic compounds that emit light when electricity is applied, and because they are thin and lightweight, they can easily be bent or shaped. AMOLED technology offers even more flexibility by incorporating a thin-film transistor layer that allows for greater control over each pixel.
Key Factors Involved in Display Curvature:
- Material Properties: OLED and AMOLED screens are made from organic materials that are flexible, making it possible to create curved displays. These materials can be thin and lightweight while retaining excellent color reproduction and clarity.
- Electrode Structure: Flexible displays use special electrode materials that allow current to flow even when the display is bent or curved. This ensures that the screen continues to function normally, even in its curved form.
- Polymer Substrates: Traditional displays use rigid glass, but flexible displays use polymer-based substrates, which allow them to bend without breaking. These substrates are both flexible and durable, offering a perfect balance for curved displays.
- Thin-Film Transistors (TFT): TFTs are used in the backplane of the flexible display to control the individual pixels. These are built into the polymer substrates, making it possible to bend or fold the display without affecting its performance.
As a result, these technologies enable displays that can be curved around edges, folded in half, or even rolled up like a piece of paper. The curvature can be applied to enhance the user experience or to create unique designs.
The Science Behind Viewing Angles in Flexible Displays
Viewing angles refer to the optimal angles from which the display can be viewed without distortion, loss of clarity, or color fading. With flexible displays, viewing angles become particularly important, especially when the display is curved. Understanding how viewing angles are affected by the curvature of the display can help improve the user experience.
Flexible displays can achieve superior viewing angles due to the following scientific principles:
- Pixel Structure and Light Emission: In traditional LCD displays, light is emitted from a backlight source and then passes through various layers to create the image. However, in OLED displays, each pixel emits its own light, which results in superior color contrast and brightness.
- Viewing Angle Optimization: Flexible displays often use advanced technologies to ensure that the display maintains high-quality images from various angles. For example, OLED technology provides wide viewing angles, meaning users can view the display from a wide range of positions without experiencing a significant drop in image quality.
- Curvature and Angle Perception: When a flexible display is curved, the angle from which the user views the screen changes depending on their position. A slight curve can make the display more immersive, enhancing the viewing experience by reducing distortion. However, too much curvature can cause certain areas of the screen to be viewed from angles where color fading and distortion might occur.
How Curvature Impacts Viewing Angles
The relationship between curvature and viewing angles is a delicate balance. Curved displays, especially those with a slight curve (like the Samsung Galaxy Fold or LG OLED curved TVs), offer a more natural viewing experience by minimizing distortion and providing a broader field of view. However, extreme curvature (such as in the wraparound displays of some smartphones) can lead to issues with color shifting and pixel distortion at certain angles of best portable monitor for laptop.
In general, the more gradual the curve, the better the viewing angles. Curves that are too aggressive can cause problems with parallax, where objects on the screen may appear warped or stretched at certain angles. To counteract this, manufacturers test and optimize the curvature and pixel arrangement to ensure that users can enjoy consistent image quality, whether the display is curved, folded, or viewed from the side.
Future Trends in Flexible Display Curvature and Viewing Angles
As technology advances, we can expect even more innovation in flexible displays, with improvements in curvature and viewing angles. Some of the potential future trends include:
- Ultra-wide Curved Displays: Expect more devices with ultra-wide or edge-to-edge flexible displays that offer immersive experiences, particularly in televisions and gaming.
- Enhanced OLED Materials: Future developments in OLED and AMOLED technologies will likely improve the color accuracy and viewing angles, even in highly curved displays.
- Foldable and Rollable Displays: We are already seeing flexible displays used in foldable and rollable devices. As the materials and technology improve, we will likely see larger, more practical rollable screens with improved durability and optimal viewing angles.
Conclusion
The science behind flexible display curvature and viewing angles is a blend of cutting-edge materials and innovative technology that allows for a more immersive, adaptable, and visually appealing user experience.
By utilizing flexible OLED and AMOLED technology, manufacturers are able to create displays that offer a perfect balance of curvature and optimal viewing angles, revolutionizing devices across industries.
Whether it’s a curved smartphone screen, a foldable tablet, or a rollable television, the future of flexible displays holds endless possibilities, and advancements in display technology will continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible.